AR(p) Model
A linear forecasting model that uses past values to predict the current value.
- time series package: statsmodels
- Regression with machine learning
- ex. multi-layer perceptron
- input layer — (hidden layers) —> output layer
Code Example
import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom statsmodels.tsa.ar_model import AutoRegfrom statsmodels.graphics.tsaplots import plot_pacf, plot_acf
# Generate synthetic AR(2) data: daily CTRnp.random.seed(42)n = 200time = pd.date_range(start='2024-01-01', periods=n, freq='D')ctr = np.sin(np.linspace(0,4*np.pi,n))*0.02 + 0.05 + np.random.normal(scale=0.005, size=n)
df = pd.DataFrame({'date': time, 'ctr': ctr})df.set_index('date', inplace=True)
df['ctr'].plot(title='Daily CTR', figsize=(10, 4))plt.show()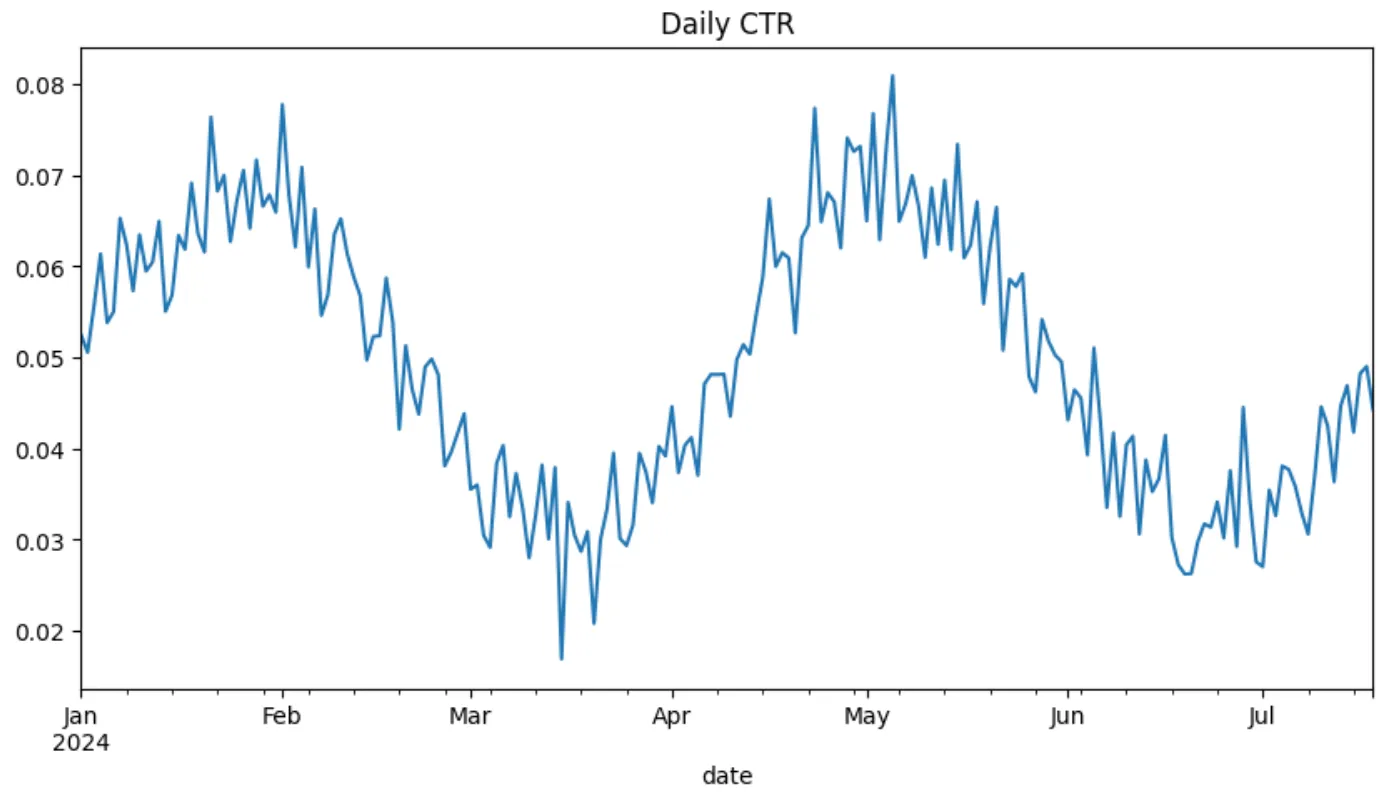
# Plot PACFplot_acf(df['ctr'], lags=30)plt.show()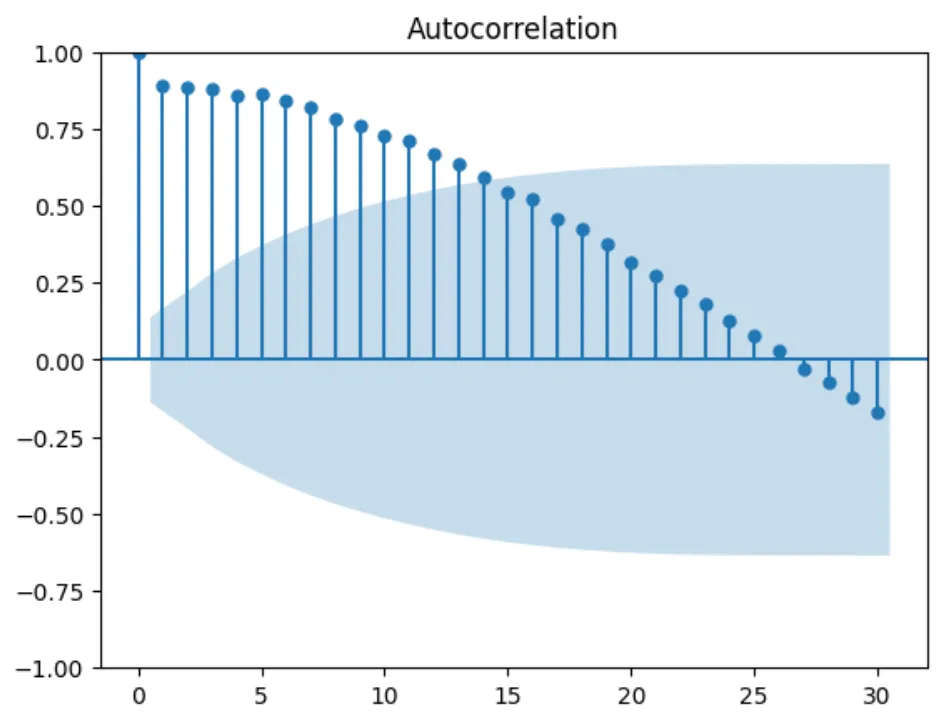
train_size = int(len(df) * 0.8)train, test = df.iloc[:train_size], df.iloc[train_size:]
# Fit AR modelmodel = AutoReg(train['ctr'], lags=17) # AR(17)model_fit = model.fit()
# Make predictionspredictions = model_fit.predict(start=len(train), end=len(train)+len(test)-1, dynamic=False)
# Plot resultsplt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))plt.plot(train.index, train['ctr'], label='Train')plt.plot(test.index, test['ctr'], label='Test')plt.plot(test.index, predictions, label='Predictions', color='red')plt.legend()plt.title('AR Model Predictions')plt.show()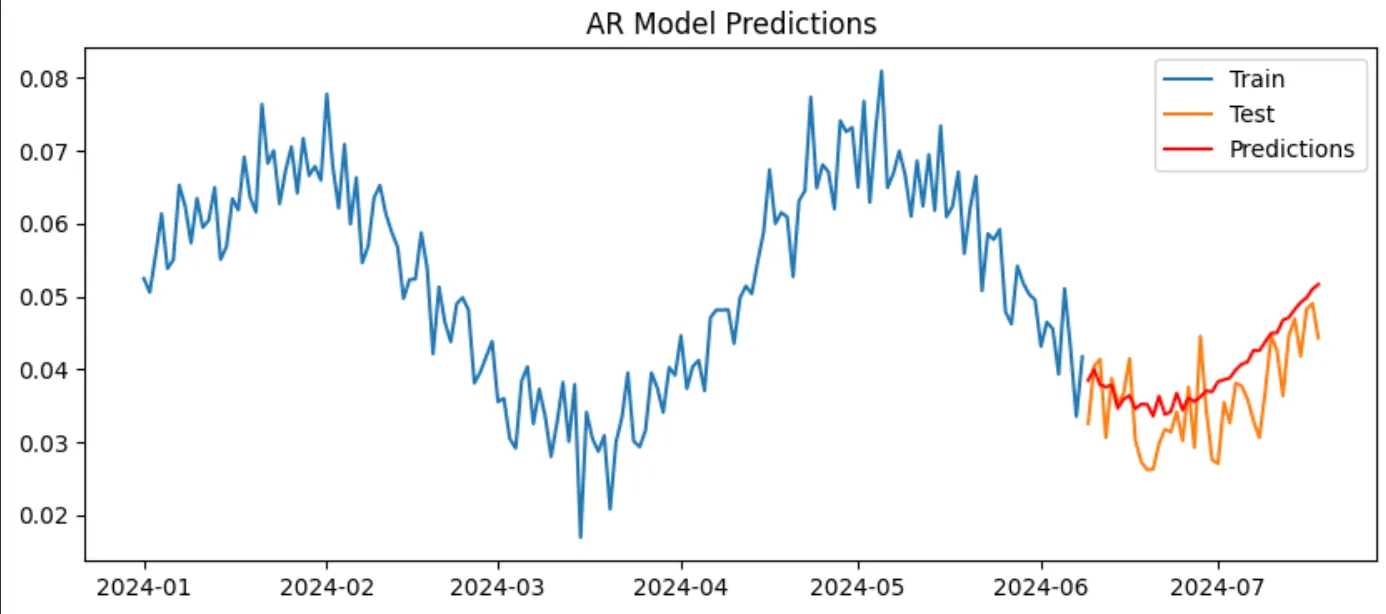
# exogenous variables (day of weeks)exog = pd.get_dummies(df.index.dayofweek)exog.columns = ['Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri', 'Sat', 'Sun']exog.index = df.index
train_exog, test_exog = exog.iloc[:train_size], exog.iloc[train_size:]
# Fit AR model with exogenous variablesmodel_exog = AutoReg(train['ctr'], lags=17, exog=train_exog)model_exog_fit = model_exog.fit()
# Make predictions with exogenous variablespredictions_exog = model_exog_fit.predict(start=len(train), end=len(train)+len(test)-1, exog_oos=test_exog, dynamic=False)
# Plot resultsplt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))plt.plot(train.index, train['ctr'], label='Train')plt.plot(test.index, test['ctr'], label='Test')plt.plot(test.index, predictions_exog, label='Predictions with Exog', color='green')plt.legend()plt.title('AR Model Predictions with Exogenous Variables')plt.show()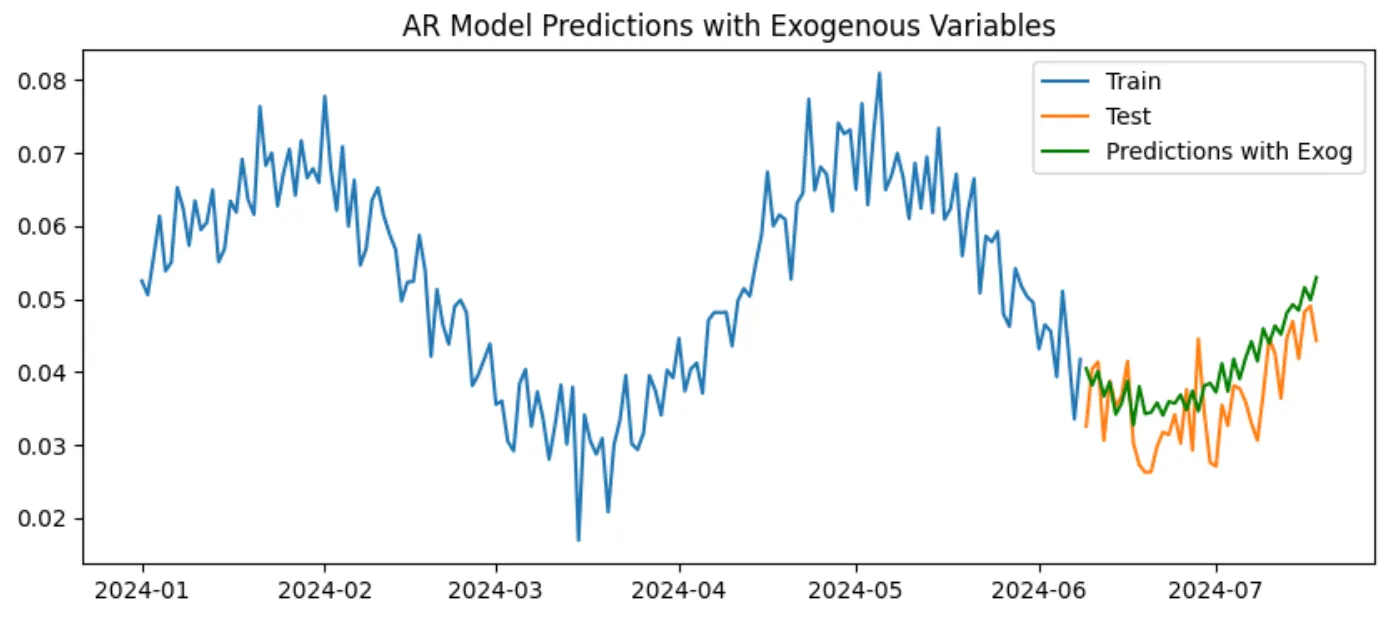
Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) for Time Series
The goal is the find the weights that minimize the loss function (e.g., Mean Squared Error).
Structure:
- Input layer: past values (lags)
- Hidden layers: non-linear transformations
- Activation functions (ReLU, Sigmoid, Tanh):
- ReLU:
- Sigmoid:
- Tanh:
- Activation functions (ReLU, Sigmoid, Tanh):
- Output layer: predicted value
Training:
- Forward pass: compute predictions
- Compute output: where are weights, is bias, and is activation function
- Compute loss: (e.g., MSE: )
- Backward pass: compute gradients and update weights using optimization algorithms (e.g., SGD, Adam)
- This is known as backpropagation
- Compute gradients using chain rule
- Update weights: where is the learning rate and is the gradient of the loss function with respect to weights
- Repeat until convergence
Importance of lags
Note
There is a trade-off between historical information and total sample size!
For too many lags, the effective sample size decreases since we lose the first observations.
Lag determines the number of input nodes!
Lag—a hyperparameter—determines the input structure, the amount of historical information used to predict the current value, making it perhaps the most crucial hyperparameter in time series forecasting with MLPs.
Code Example
import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(42)
n = 365time = pd.date_range(start='2023-01-01', periods=n, freq='D')ctr = np.sin(np.linspace(0, 4 * np.pi, n)) * 0.02 + 0.05 + np.random.normal(scale=0.005, size=n)
df = pd.DataFrame({'date': time, 'ctr': ctr})
df.set_index('date', inplace=True)
df['ctr'].plot(title='Daily CTR', figsize=(10, 5))
plt.show()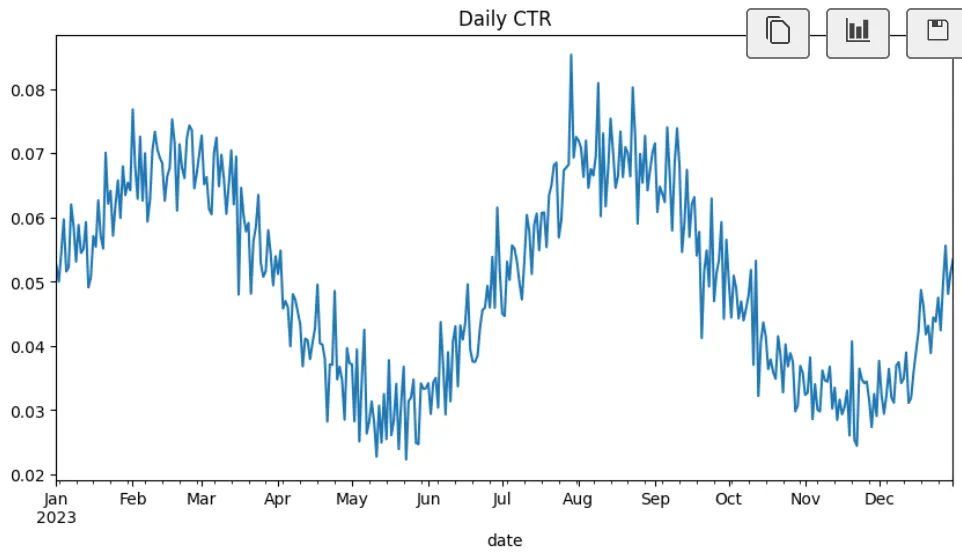
ctr_min = df['ctr'].min()ctr_max = df['ctr'].max()
# normalizationdf['ctr'] = (df['ctr'] - ctr_min) / (ctr_max - ctr_min)df['ctr'].plot(figsize=(10, 5))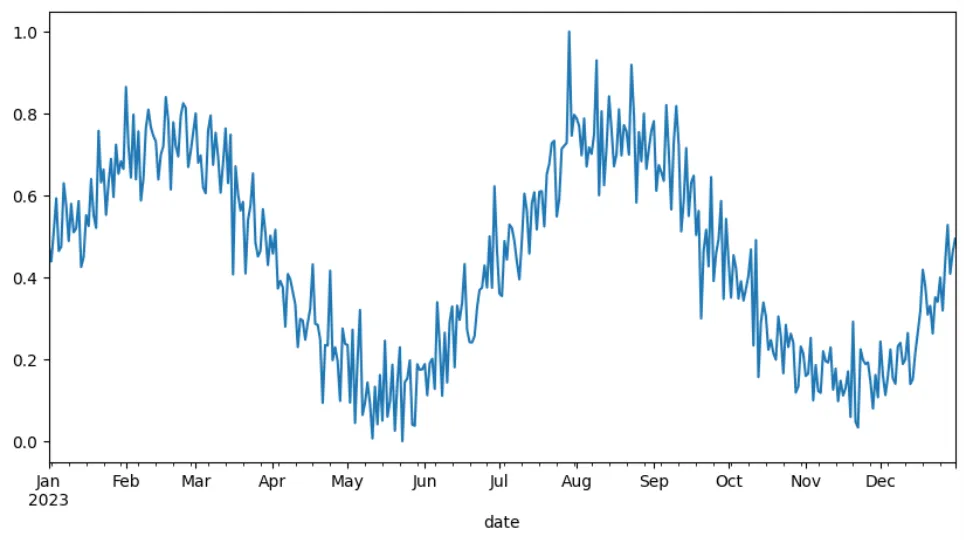
def create_lagged_data(series, lags=5): X, y = [], [] for i in range(len(series)- lags): X.append(series[i:i+lags]) y.append(series[i+lags]) return np.array(X), np.array(y)
X_test, y_test = create_lagged_data(df['ctr'].values, lags=2)
for i in range(10): print(X_test[i], '->', y_test[i])
lags = 17X, y = create_lagged_data(df['ctr'].values, lags=lags)
split = int(len(X) * 0.8)X_train, y_train = X[:split], y[:split]X_test, y_test = X[split:], y[split:]
train_dates = df.index[lags:split+lags]test_dates = df.index[split+lags:]
# len(y_train), len(train_dates)
def intialize_weights(input_size, hidden_size, output_size): weights_input_hidden = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (input_size, hidden_size)) weights_hidden_output = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (hidden_size, output_size)) bias_hidden = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (1, hidden_size,)) bias_output = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, (1, output_size,)) return weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output
def relu(x): return np.maximum(0, x)
def relu_derivative(x): return np.where(x > 0, 1, 0)
def mse_loss(y_true, y_pred): return np.mean((y_true - y_pred) ** 2)
def forward_pass(X, weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output): hidden_input = np.dot(X, weights_input_hidden) + bias_hidden hidden_output = relu(hidden_input) final_input = np.dot(hidden_output, weights_hidden_output) + bias_output final_output = final_input # Linear activation for output layer return hidden_output, final_output
def backward_pass(X, y, hidden_output, final_output, weights_hidden_output): output_error = final_output - y # 교수님은 y - final_output으로 하긴 함,, output_delta = output_error # Derivative of linear activation is 1
hidden_error = np.dot(output_delta, weights_hidden_output.T) # *2 in class hidden_delta = hidden_error * relu_derivative(hidden_output)
return output_delta, hidden_delta
def update_weights(X, hidden_output, output_delta, hidden_delta, weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output, learning_rate): weights_hidden_output -= np.dot(hidden_output.T, output_delta) * learning_rate weights_input_hidden -= np.dot(X.T, hidden_delta) * learning_rate bias_output -= np.sum(output_delta, axis=0, keepdims=True) * learning_rate bias_hidden -= np.sum(hidden_delta, axis=0, keepdims=True) * learning_rate return weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output
def train_mlp(X, y, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, epochs=1000, learning_rate=0.001): weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output = intialize_weights(input_size, hidden_size, output_size)
for epoch in range(epochs): hidden_output, final_output = forward_pass(X, weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output)
loss = mse_loss(y, final_output)
output_delta, hidden_delta = backward_pass(X, y, hidden_output, final_output, weights_hidden_output)
weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output = update_weights(X, hidden_output, output_delta, hidden_delta, weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output, learning_rate)
if epoch % 100 == 0: print(f'Epoch {epoch}, Loss: {loss}')
return weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output
def predict(X, weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output): _, final_output = forward_pass(X, weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output) return final_output
input_size = lagshidden_size = 10output_size = 1weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output = train_mlp(X_train, y_train.reshape(-1, 1), input_size, hidden_size, output_size, epochs=1000, learning_rate=0.001)
predictions = predict(X_test, weights_input_hidden, weights_hidden_output, bias_hidden, bias_output)predictions = predictions.flatten()y_test = y_test.flatten()Output:
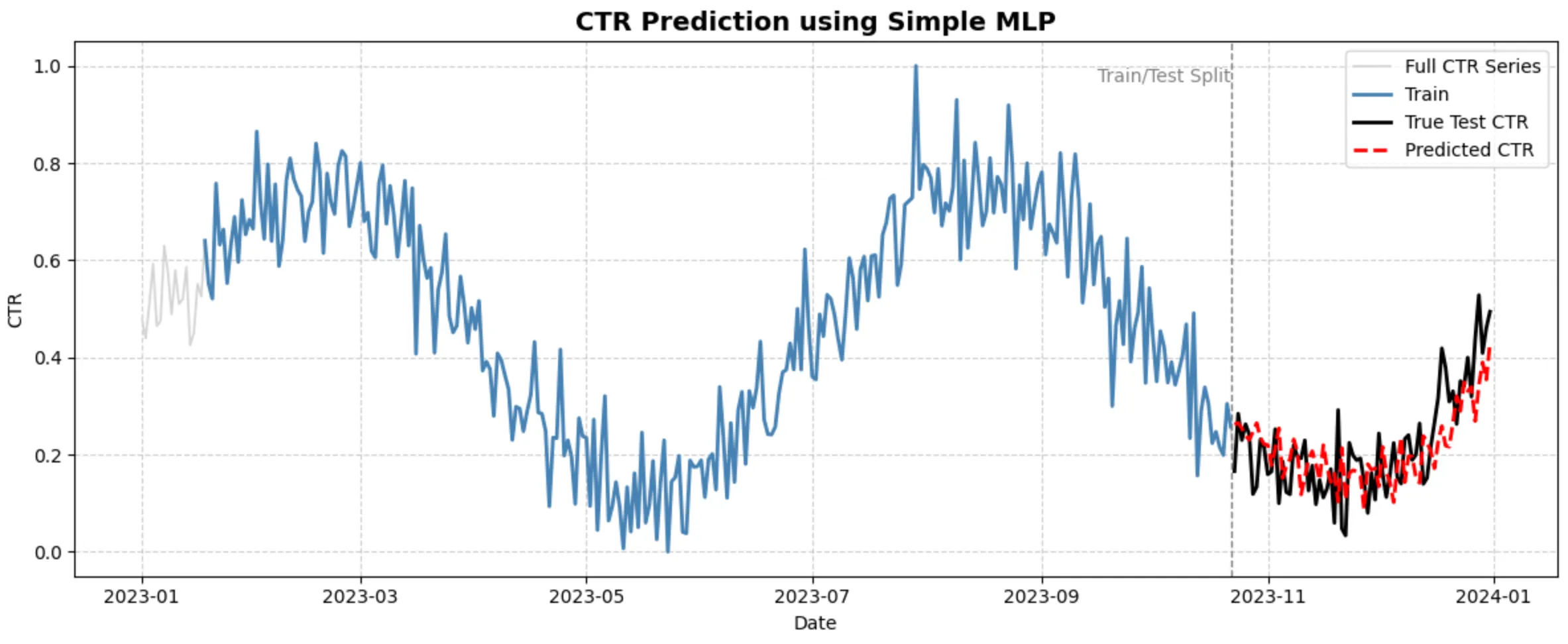
Epoch 0, Loss: 5.632162843223016Epoch 100, Loss: 0.05115925220822442Epoch 200, Loss: 0.04275551312820102Epoch 300, Loss: 0.02245051661551441Epoch 400, Loss: 0.018830809997783342Epoch 500, Loss: 0.016457206995812355Epoch 600, Loss: 0.014710278047137417Epoch 700, Loss: 0.013191127588598398Epoch 800, Loss: 0.012093276219005963Epoch 900, Loss: 0.011152334762943965plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))plt.plot(df.index, df['ctr'], color='lightgray', label='Full CTR Series', linewidth=1.2)plt.plot(train_dates, y_train, color='steelblue', label='Train', linewidth=2)plt.plot(test_dates, y_test, color='black', label='True Test CTR', linewidth=2)plt.plot(test_dates, predictions, color='red', linestyle='--', label='Predicted CTR', linewidth=2)
plt.axvline(x=train_dates[-1], color='gray', linestyle='--', linewidth=1)plt.text(train_dates[-1], plt.ylim()[1]*0.95, 'Train/Test Split', ha='right', va='top', fontsize=10, color='gray')
plt.title('CTR Prediction using Simple MLP', fontsize=14, weight='bold')plt.xlabel('Date')plt.ylabel('CTR')plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.6)plt.legend()plt.tight_layout()plt.show()