Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
PSO is a population-based optimization technique inspired by the social behavior of birds flocking or fish schooling. Each particle represents a potential solution and adjusts its position based on its own experience and that of neighboring particles. It is also a metaheuristic algorithm.
Terminology
- Particle: Represents a potential solution in the search space.
- Velocity: The rate of change of the particle’s position.
- Defined by inertia, individual best, and swarm best.
- Position: The current location of the particle in the search space.
- Personal Best (pBest): The best position a particle has achieved so far.
- Global Best (gBest): The best position achieved by any particle in the swarm.
- Inertia Weight: A parameter that controls the impact of the previous velocity on the current velocity.
Algorithm Steps
- Initialization
- Initialize a population of particles with random positions and velocities.
- Set the initial pBest for each particle to its starting position.
- Set the initial gBest to the best pBest among all particles.
- Velocity Update
-
Update the velocity of each particle based on its current velocity, the distance to its pBest, and the distance to the gBest.
-
The velocity update formula is given by:
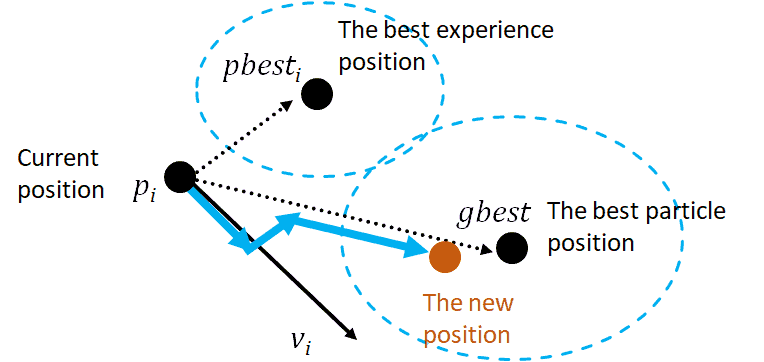
where:
- : Velocity of particle (i) at time (t)
- : Position of particle (i) at time (t)
- : Inertia weight (controls the impact of the previous velocity)
- : Cognitive and social coefficients (control the influence of pBest and gBest)
- : Random numbers between 0 and 1
-
- Position Update
- Update the position of each particle based on its new velocity.
- The position update formula is given by:
- Fitness Evaluation
- Evaluate the fitness of each particle’s new position using the objective function.
- If the new position is better than the particle’s pBest, update pBest.
- If the new pBest is better than the current gBest, update gBest.
- Termination
- Repeat steps 2-4 until a stopping criterion is met (e.g., a maximum number of iterations or a satisfactory fitness level).
Code Practice
Given Problem:
import numpy as np
def pso_LP(c, A, b, swarm_size=40, max_iter=200, w=0.75, c1=1.5, c2=1.5, penalty_scale=1e5): """ Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) for Linear Programs: max c^T x s.t. A x <= b, x >= 0
Parameters ---------- c : array_like Coefficients of the objective function (shape: n,) A : array_like Constraint matrix (shape: m, n) b : array_like RHS of constraints (shape: m,) swarm_size : int Number of particles max_iter : int Number of iterations w, c1, c2 : float Inertia, cognitive, and social coefficients penalty_scale : float Large penalty for constraint violations
Returns ------- gbest_position : ndarray Best solution found gbest_obj : float Objective value at best solution """
# Convert inputs c = np.asarray(c, dtype=float).reshape(-1) A = np.asarray(A, dtype=float) b = np.asarray(b, dtype=float).reshape(-1) m, n = A.shape
# Random initialization (x >= 0) pos = np.random.rand(swarm_size, n) * (b.max() / (A.max() + 1e-9)) vel = np.random.randn(swarm_size, n)
# Fitness evaluation def fitness(x): # objective obj = np.dot(c, x) # constraints violation (Ax <= b) violation = np.maximum(A @ x - b, 0.0) penalty = penalty_scale * violation.sum() return obj - penalty
# Initialize personal bests pbest = pos.copy() pbest_val = np.array([fitness(x) for x in pos])
# Initialize global best gbest_idx = np.argmax(pbest_val) gbest = pbest[gbest_idx].copy() gbest_val = pbest_val[gbest_idx]
# Main loop for t in range(max_iter): for i in range(swarm_size): fval = fitness(pos[i]) if fval > pbest_val[i]: pbest[i] = pos[i].copy() pbest_val[i] = fval
# Update global best if np.max(pbest_val) > gbest_val: gbest_idx = np.argmax(pbest_val) gbest = pbest[gbest_idx].copy() gbest_val = pbest_val[gbest_idx]
# Update velocities and positions r1, r2 = np.random.rand(swarm_size, n), np.random.rand(swarm_size, n) vel = (w * vel + c1 * r1 * (pbest - pos) + c2 * r2 * (gbest - pos)) pos = pos + vel pos = np.clip(pos, 0, None) # enforce x >= 0
return gbest, gbest_val
# Define your problemc = [40, 30]A = [[2, 1], [1, 1], [1, 0]]b = [100, 80, 40]
best_x, best_val = pso_LP(c, A, b)print("Best solution (x, y):", best_x)print("Objective value:", best_val)
# Output:# Best solution (x, y): [19.99999995 59.99999999]# Objective value: 2599.999997587528Professor’s Code Version
This version is a little more robust, and has a stronger penalty for constraint violations.
import numpy as np
def pso_LP(c, A, b, swarm_size=40, max_iter=200, w=0.75, c1=1.5, c2=1.5, penalty_scale=1e5): """ Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) for LP: max c^T x s.t. A x <= b, x >= 0 """
# Convert inputs c = np.asarray(c, dtype=float).reshape(-1) A = np.asarray(A, dtype=float) b = np.asarray(b, dtype=float).reshape(-1) m, n = A.shape
# Bounds [0, 80] (example upper bound; adjust if needed) bounds = [0, 80]
# Initialize particles positions = np.random.uniform(low=bounds[0], high=bounds[1], size=(swarm_size, n)) velocities = np.random.uniform(-0.05, 0.05, size=(swarm_size, n))
# Penalized objective (we MINIMIZE) def penalized_obj(x_vec): base = -np.dot(c, x_vec) # negate for maximization ineq_viol = np.maximum(0.0, np.dot(A, x_vec) - b) # Ax <= b nonneg_viol = np.maximum(0.0, -x_vec) # x >= 0 penalty = penalty_scale * (np.sum(ineq_viol**2) + np.sum(nonneg_viol**2)) return base + penalty
# Personal and global bests pbest_positions = positions.copy() pbest_scores = np.array([penalized_obj(positions[i]) for i in range(swarm_size)]) gbest_index = np.argmin(pbest_scores) gbest_position = pbest_positions[gbest_index].copy() gbest_score = float(pbest_scores[gbest_index])
# Main loop for iteration in range(max_iter): for i in range(swarm_size): score = penalized_obj(positions[i])
# Update personal best if score < pbest_scores[i]: pbest_scores[i] = score pbest_positions[i] = positions[i].copy()
# Update global best if score < gbest_score: gbest_score = score gbest_position = positions[i].copy()
# Update velocities and positions for i in range(swarm_size): r1, r2 = np.random.rand(n), np.random.rand(n) velocities[i] = (w * velocities[i] + c1 * r1 * (pbest_positions[i] - positions[i]) + c2 * r2 * (gbest_position - positions[i])) positions[i] = positions[i] + velocities[i] # Keep inside bounds positions[i] = np.clip(positions[i], bounds[0], bounds[1])
# Return best solution (convert back from minimized form) gbest_obj = float(np.dot(c, gbest_position)) return gbest_position, gbest_obj
# Define your problemc = [40, 30]A = [[2, 1], [1, 1], [1, 0]]b = [100, 80, 40]
best_x, best_val = pso_LP(c, A, b)print("Best solution (x, y):", best_x)print("Objective value:", best_val)
# Output:# Best solution (x, y): [19.99995011 60.00014982]# Objective value: 2600.0024989010058HPO with PSO
This is the same problem solved with genetic algorithms in the previous lecture.
Given Problem:
Use the following assumptions to generate the dataset:
- True model:
- : Generate 100 random values.
- : Generate 100 values with the above and add error with a normal distribution.
- e.g.
- Use the same loss function on the upper and lower level.
- Ridge regression loss:
import numpy as npfrom sklearn.linear_model import Ridgefrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport random
# Generate synthetic datax = np.random.rand(100)y = 2 * x + 1 + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, size=x.shape)
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(x, y, train_size=0.8)
# Lower-level: Ridge regressiondef lower_opt(x_train, y_train, lambda_val): model = Ridge(alpha=lambda_val) model.fit(x_train, y_train) m = model.coef_ b = model.intercept_ return m, b
# Upper-level: Evaluate on validation setdef upper_eval(x_val, y_val, m, b, lambda_val): obj = sum((y_val[i] - (m * x_val[i] + b))**2 for i in range(len(y_val))) + lambda_val * m**2 obj = obj[0] # because sum returns numpy array w/ shape (1,) return obj
# PSO for HPOdef pso_HPO(x_train, y_train, x_val, y_val, swarm_size=20, max_iter=50, w=0.7, c1=1.5, c2=1.5): # Initialize particles (λ values between 0.0001 and 1) positions = np.random.uniform(0.0001, 1, size=swarm_size) velocities = np.random.uniform(-0.05, 0.05, size=swarm_size)
# Personal and global bests personal_best_positions = positions.copy() personal_best_scores = np.full(swarm_size, np.inf) global_best_position = positions[0] global_best_score = np.inf
for _ in range(max_iter): for i in range(swarm_size): m, b = lower_opt(x_train, y_train, positions[i]) score = upper_eval(x_val, y_val, m, b, positions[i])
# Update personal best if score < personal_best_scores[i]: personal_best_scores[i] = score personal_best_positions[i] = positions[i]
# Update global best if score < global_best_score: global_best_score = score global_best_position = positions[i]
# Update velocities and positions r1, r2 = np.random.rand(swarm_size), np.random.rand(swarm_size) velocities = (w * velocities + c1 * r1 * (personal_best_positions - positions) + c2 * r2 * (global_best_position - positions)) positions += velocities
# Keep λ within bounds [0.0001, 1] positions = np.clip(positions, 0.0001, 1)
return global_best_position
# Run PSO for HPObest_lambda_pso = pso_HPO(x_train.reshape(-1,1), y_train, x_val.reshape(-1,1), y_val)
final_model = Ridge(alpha=best_lambda_pso)final_model.fit(x_train.reshape(-1,1), y_train)
print(f"PSO 최적 λ: {best_lambda_pso:.4f}")
# Plot resultsplt.scatter(x, y, color='blue', label='Data')plt.plot(x, final_model.coef_ * x + final_model.intercept_, color='red', label=f'Ridge Regression (λ={best_lambda_pso:.4f})')plt.xlabel('x')plt.ylabel('y')plt.title('Ridge Regression with PSO-optimized λ')plt.legend()plt.grid()plt.show()